N2 Benchmark¶
This page is a detailed explanation of how we performed benchmark experiments.
You can also see benchmarks of ANN libraries in Python at ann-benchmarks.com. Note that N2 version 0.1.6 is used in ann-benchmarks.com (last checked on October 8th, 2020) and we are continuing our efforts to improve N2 performance.
Benchmark Focus¶
These are some factors that we focus on when developing N2.
Our ANN algorithm should run fast even when dealing with large-scale datasets.
Our ANN algorithm should minimize the time required to build an index file - in order to be applied to real-world scenario where dataset changes frequently (e.g. create/update/delete), such as in online content services like news portal.
Therefore, our main criteria for benchmark are set as below:
How long does it take to build the index file?
How long does it take to get results from the large dataset?
How large memory does it take to run large dataset?
Test Dataset¶
Dataset Description¶
To test large amounts of data, we use youtube dataset that
contains 14520986 samples, where each sample has 40 data points.
feature1(float32) |
feature2(float32) |
…… |
feature2(float32) |
feature40(float32) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
-0.167898 |
0.160478 |
…… |
0.104421 |
0.0503584 |
How to Download the Benchmark Dataset¶
You can download benchmark dataset with the script we provide in Download dataset.
We also share youtube dataset through google
drive.
It consists of two plain text files, youtube.txt and youtube.txt.vids.
youtube.txt is a file containing the information of dataset samples
and youtube.txt.vids is a file containing the dataset metadata information.
Each line is the metadata corresponding to each sample in youtube.txt.
DSID |
VID |
Youtube link |
|---|---|---|
34XnPr4YKpo8wE_mEl |
Z1Jilm0TZHY |
Test Environment¶
CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2620 v4
Memory: 64GB
Storage: SSD
Dataset: Youtube(5.4GB)
N2 version: 0.1.7
NMSLIB version: 2.0.6
g++ (gcc): 7.3.1
Index Build Time¶
The following is a comparison of the index build times taken when using different numbers of threads. N2 builds index file 10~24% faster than NMSLIB.
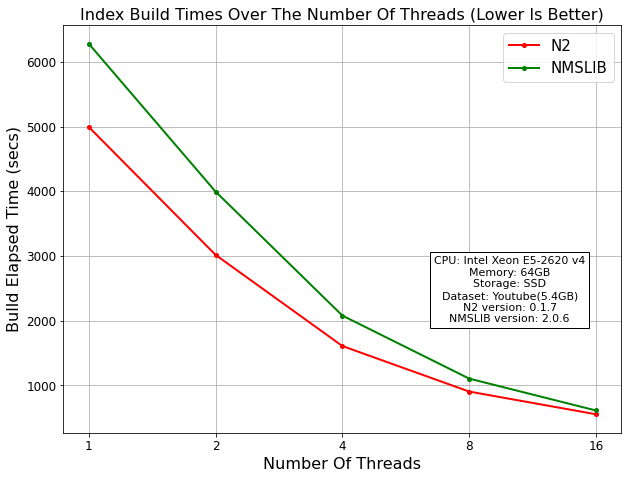
Library |
1 Thread |
2 Threads |
4 Threads |
8 Threads |
16 Threads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
N2 (Index Size: 3.7GB) |
4995.73 sec |
3018.57 sec |
1609.89 sec |
905.87 sec |
554.81 sec |
NMSLIB (Index Size: 3.9GB) |
6282.5 sec |
3996.88 sec |
2080.36 sec |
1106.18 sec |
613.18 sec |
Search Speed¶
The data below shows tradeoff between QPS(Queries Per Second) and accuracy. Both N2 and NMSLIB shows similar search performance.
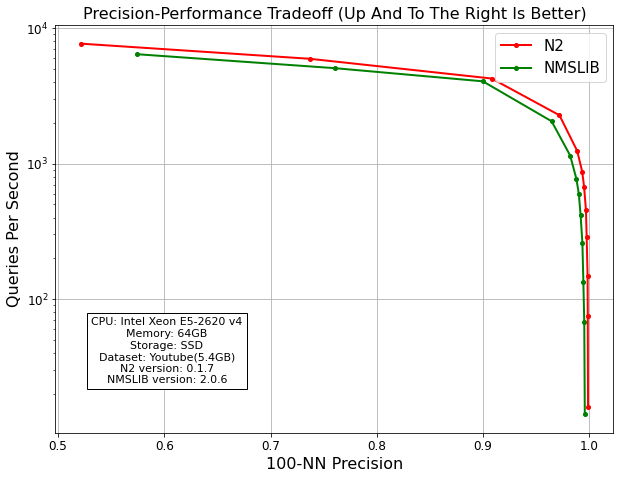
Parameter |
Search Time (N2) |
Accuracy (N2) |
Search Time (NMSLIB) |
Accuracy (NMSLIB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 25 |
0.000130227 |
0.52136 |
0.000155903 |
0.574523 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 50 |
0.000168451 |
0.736898 |
0.000197621 |
0.760703 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 100 |
0.000235572 |
0.908154 |
0.000247012 |
0.899827 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 250 |
0.000439563 |
0.971894 |
0.000486722 |
0.964502 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 500 |
0.000805385 |
0.988616 |
0.000871604 |
0.982023 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 750 |
0.00114534 |
0.993323 |
0.00129876 |
0.987889 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 1000 |
0.00148114 |
0.995105 |
0.00166815 |
0.99014 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 1500 |
0.00219379 |
0.996848 |
0.00241407 |
0.991855 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 2500 |
0.00348781 |
0.997529 |
0.00385025 |
0.993514 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 5000 |
0.00669571 |
0.99839 |
0.00744833 |
0.994425 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 10000 |
0.0132182 |
0.998577 |
0.014742 |
0.995269 |
M: 12, efCon: 100, efSearch: 50000 |
0.0627954 |
0.998814 |
0.0706788 |
0.995788 |
Memory Usage¶
The data below shows the amount of memory used to build the index file, which is measured as the difference between memory usage before and after building the index file. N2 uses 15% less memory than NMSLIB.
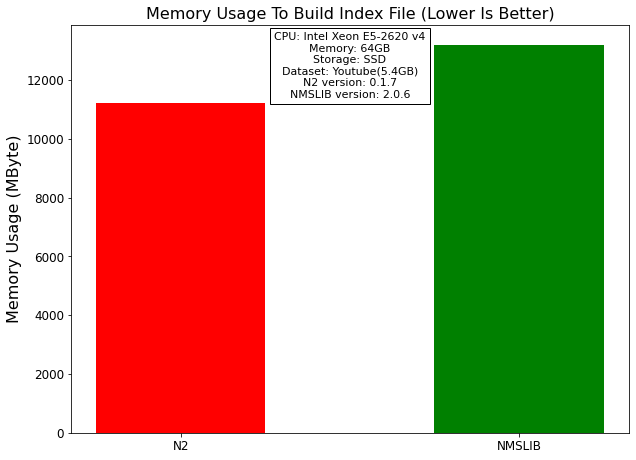
Library |
Memory Usage |
|---|---|
N2 |
11222.48 MB |
NMSLIB |
13212.76 MB |
Conclusion¶
N2 builds index file faster and uses less memory than NMSLIB, while having a similar search speed performance.
The benchmark environment uses multiple threads for index builds but a single thread for searching. In a real production environment, you will need to run concurrent searches by multiple processes or multiple threads. N2 allows you to search simultaneously using multiple processes. With mmap support in N2, it works much more efficiently than other libraries, including NMSLIB.